AIRSOL CCS-HR
Ventilation systems in large buildings (total air volume > 100 000 m3/h) are often equipped with circuit connected systems with heat recovery (CCS-HR), as air intake and output systems can be installed in different places and are not physically linked to each other. Plate and rotation heat exchangers for large air volumes per unit are difficult to implement (spatial conditions).
The application field of circuit connected systems is extensive. From primary ventilation systems for supplying building room areas to hospital buildings, laboratory buildings, chemistry, pharmacies, undercutting, pressing facilities, gantries, stores, trade fair halls, kitchens, restaurants, office buildings, biological laboratories, university buildings, administrative buildings, theatres, museums, fine mechanics production rooms and process technical room ventilation or renovations where the air intake and output cannot be installed together.
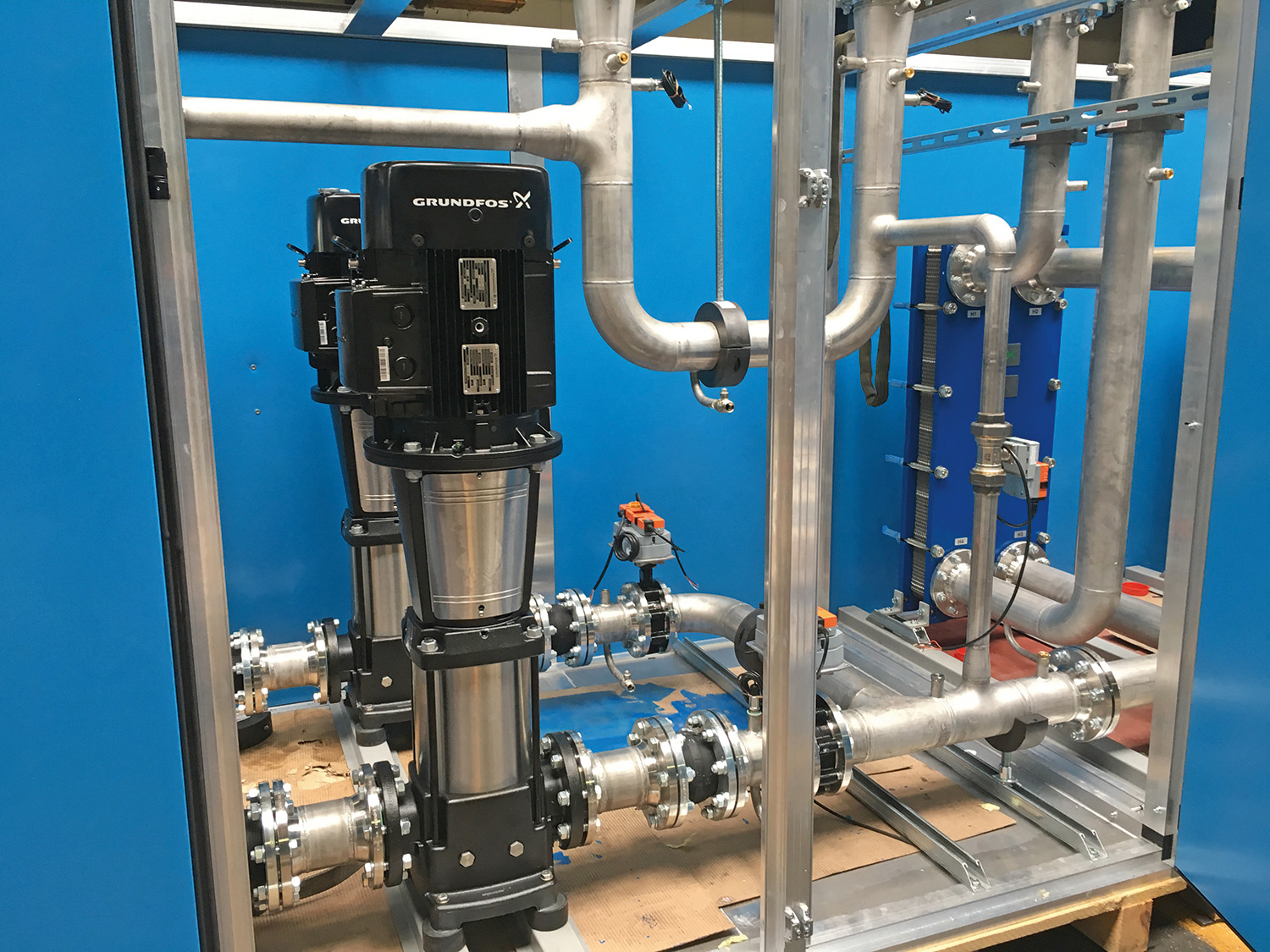
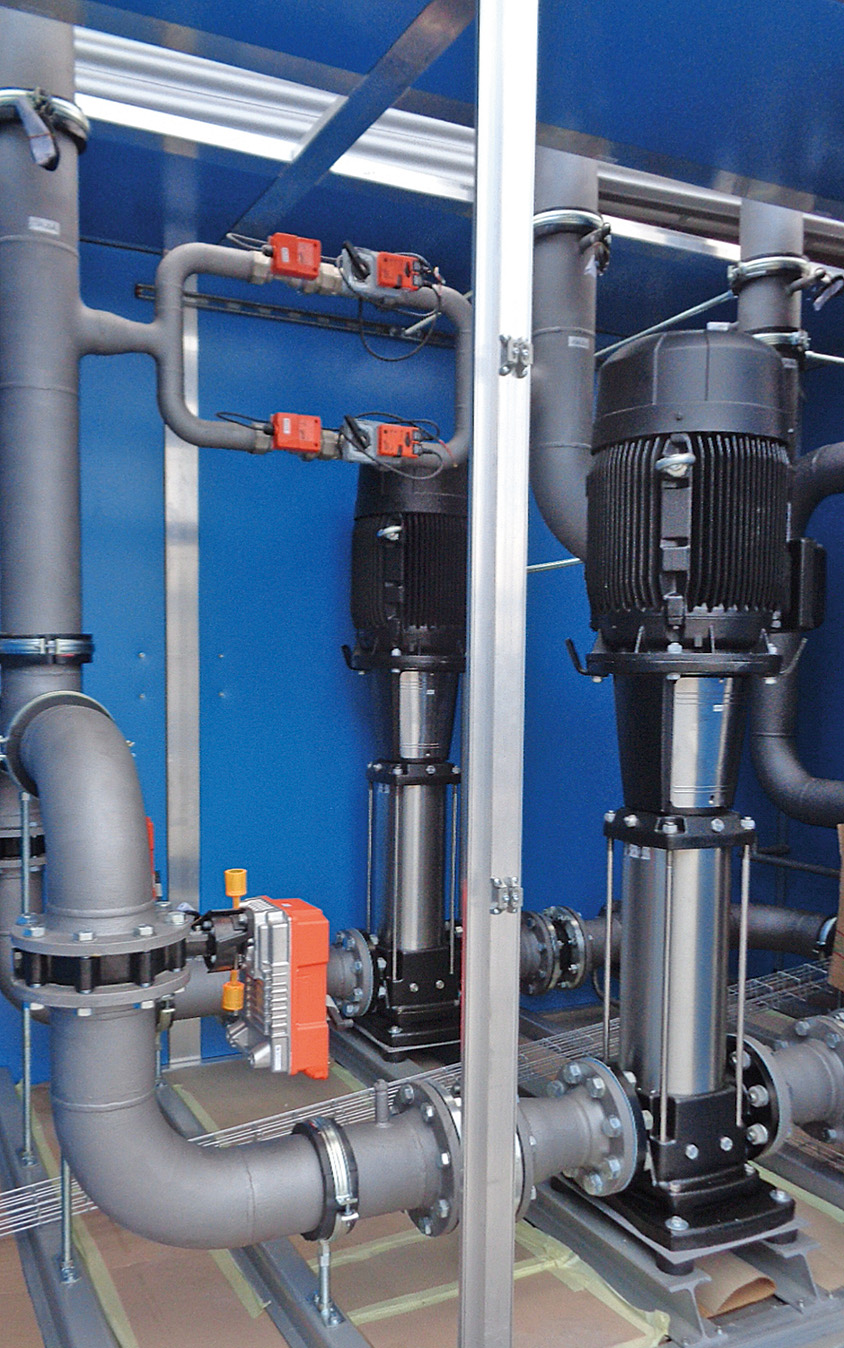
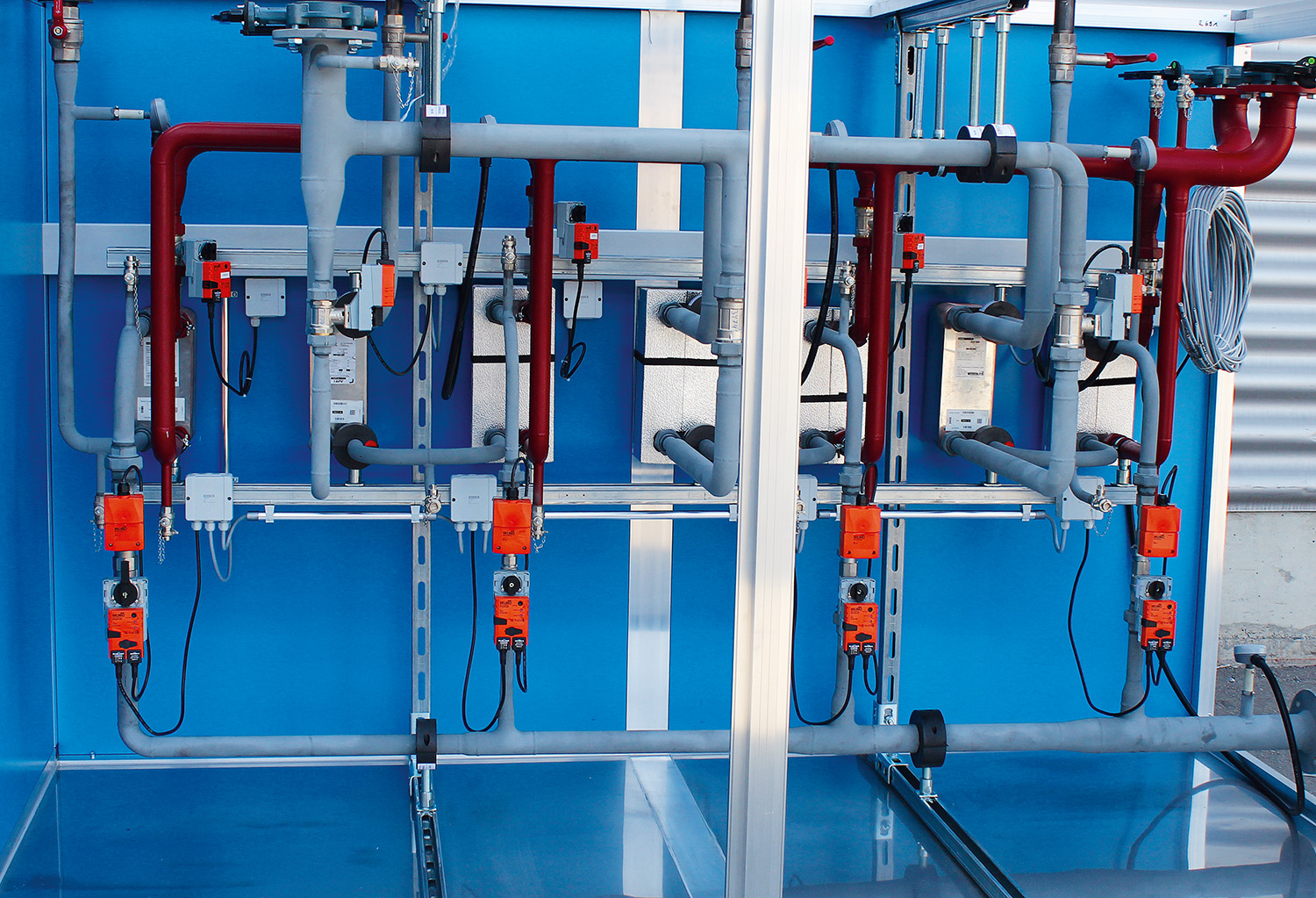
AIRSOL® high-performance CCS-HR systems work with maximum exchange degrees. On the exhaust air side, the water-glycol mixture (intermediary medium) is warmed as close as possible to the exhaust air temperature. The warmed medium then circulates to the outdoor air systems and can warm up the air from outdoors. The AIRSOL® heat exchanger also has a maximum exchange degree in this area. The correctly regulated water-glycol amount in the intermediary circuit guarantees the maximum temperature difference.
In the summer mode, the exhaust air can be humidified adiabatically, the intermediary circuit cooles down and a supply air cooling is generated. The effect is maximised through the use of Mountair hybrid cooling elements.
The lacking heat (additional heating) or cold (additional cooling) can be supplied by plate heat exchangers in the water-glycol circuit. This makes additional heat exchangers in the airflow unnecessary, and the ventilation requires less energy.
In network systems, one or more air handling units are connected. The AIRSOL® controller calculates and provides the ideal volumes of fluid and guarantees the maximum annual efficiency.
The system optimisation is ensured in all operating states. A better exchange degree also means a higher pressure drop. If the additionally spent energy reserve is more valuable than the recovered heat, the system is “maxed out”. The annual efficiency shows what percentage of the total heating energy is recovered by the CCS-HR. The consideration of the energy used for humidification and cooling is essential.
- Maximum heat recovery with separated intake and exhaust air flows
- Network systems to use decentralised exhaust heat sources
- Controller for system optimisation and energy monitoring
- Simple subsequent equipment of existing air conditioning stations for energy saving
- Cost and benefit simulation
- Defroster circuit for the outdoor air filter
- Adiabatic cooling
- Heat and cold supply in the circuit. No additional heaters or coolers needed.
- Less pressure drop, better SFP (Specific Fan Power)
- Annual efficiency (AE) and electrothermic amplification factors (EAF) in accordance with the energy ordinances
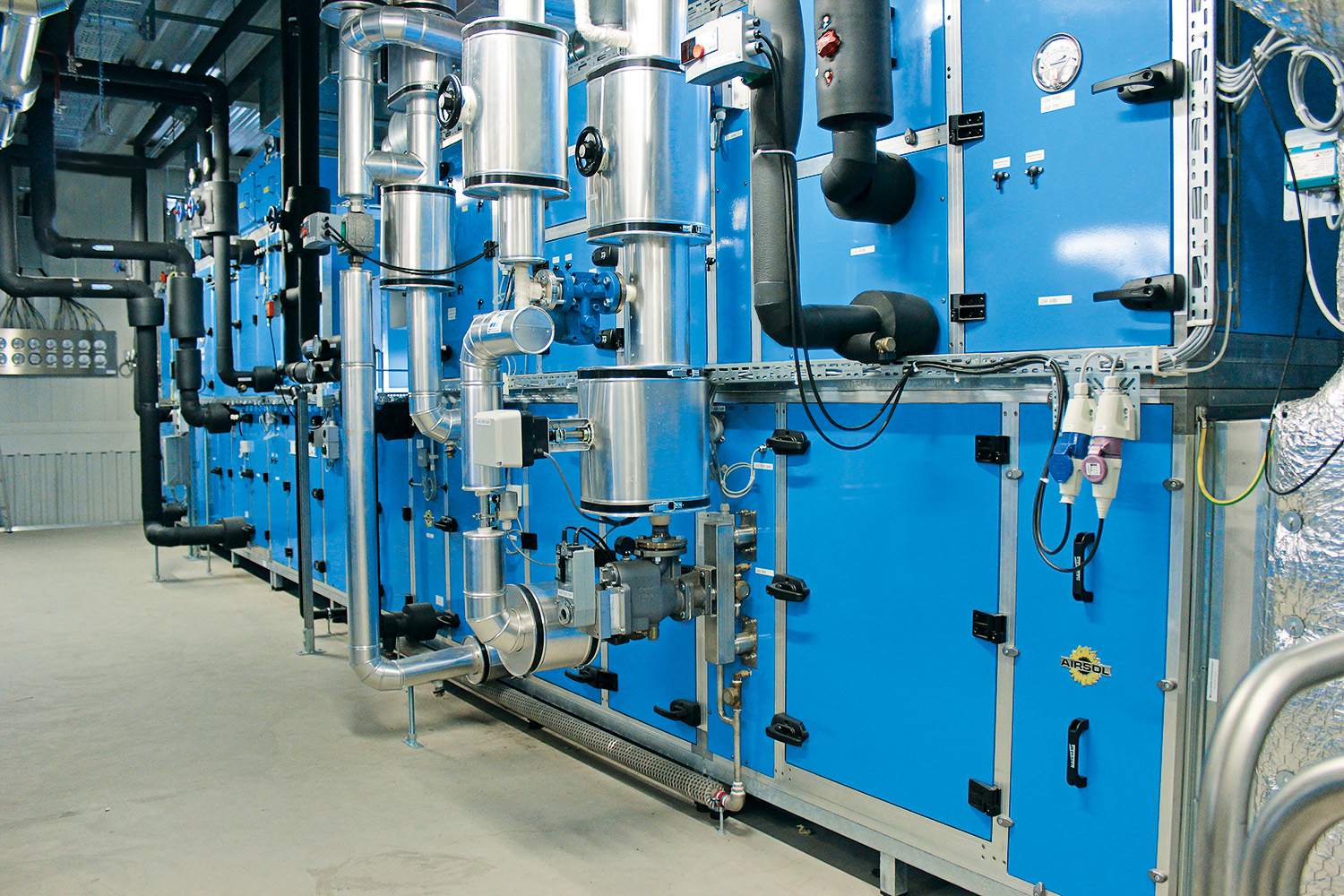
The material and production quality is in accordance with the AIRSOL® standard, i.e.:
- Pipe wall thickness Cu 0.4 mm
- Hydraulically widened (less pressure loss than with mechanical widening)
- Fin thickness min 0.2 mm
- Exchanger solely out of non-ferrous metals
- Exchanger can be fully ventilated and emptied
- Optimised AIRSOL® circuit for maximum return flow
- Pressure: PN 16
- Design according to Eurovent, consideration of hygienic aspects regarding cleaning
- External piping in steel, copper and chrome steel
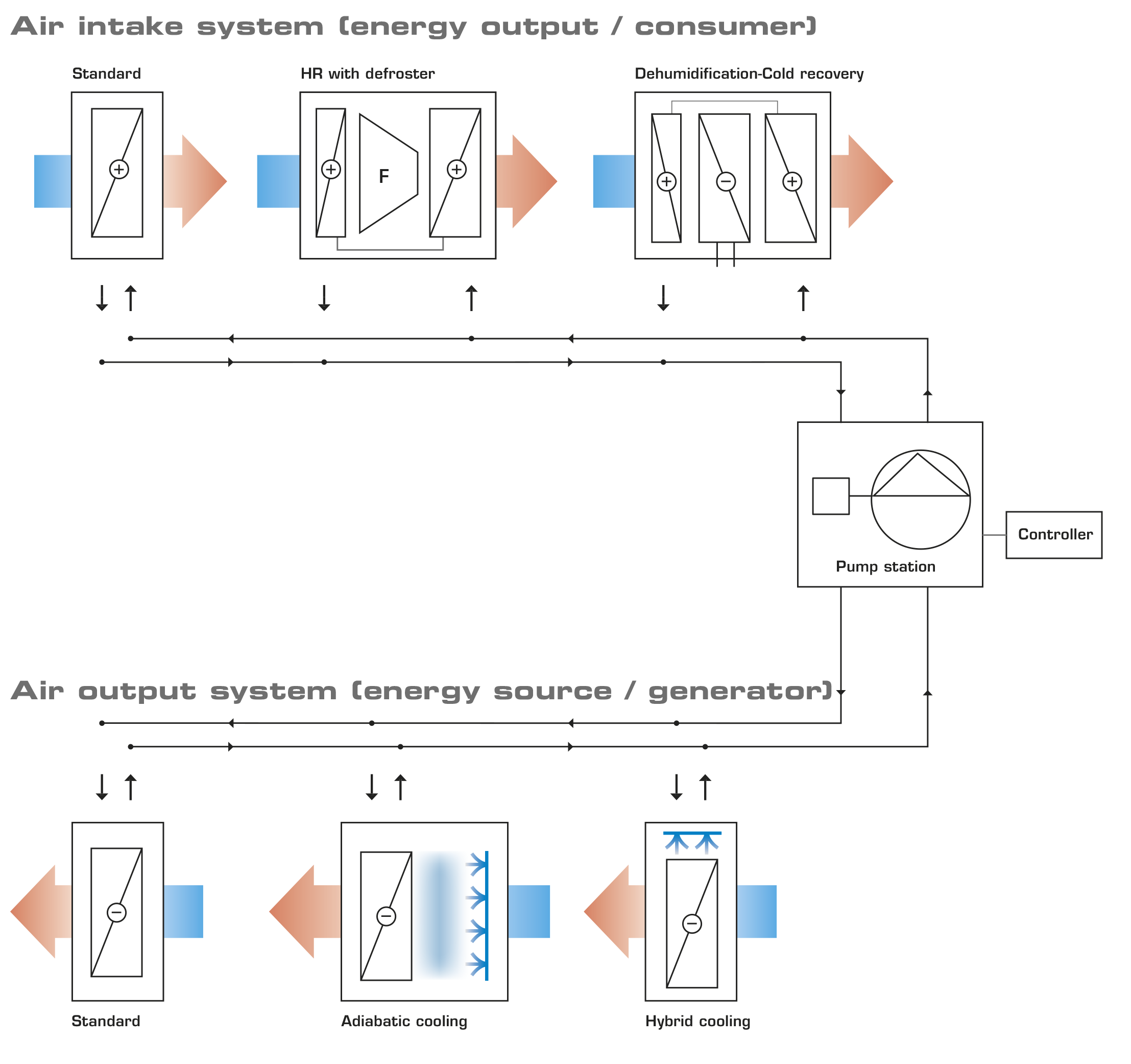
Air intake systems
Standard
AIRSOL® High-performance CCS-HR systems work with maximum exchange degrees. The standard consumer is an air intake system. The cold outdoor air is heated with heat recovery.
HR with defroster
Weather changes can lead to ice on the fresh air filters. It is therefore recommended to split the CCS heat exchanger in the fresh air between a defroster (few pipe rows, wide fin spacing) and an air heater (many pipe rows, small fin spacing) and pass the glycol through them serially (hygiene guideline). The heating in the defroster is sufficient to prevent any ice on the filter. The defroster installed in front of the filter with wide fin spacing can be cleaned without problems.
Dehumidified cold recovery
CCS3 means that the large HR battery is split into two coils. In the summer, in the drying mode, the glycol mixture circulates serially through the exchangers. In-between, the cooler is set to condensation dehumidification. The necessary additional heating is thus used for pre-cooling. The power requirement of the cooler is significantly reduced. The cooler is supplied by external refrigerating machines. Triple splitting with additional defroster.
Air output systems
Standard
On the exhaust air side, the water-glycol mixture is warmed as close as possible to the exhaust air temperature.
(Heat is removed from the exhaust air and transported to the supply air via the water-glycol mixture).
Adiabatic cooling
Adiabatic cooling via exhaust air humidification. The following humidification systems are used for this:
- Contact humidifier for operating with soft water. Circulating water with automatic desalination.
- Atomizing humidifier (high/low pressure systems). Operation with desalinised water.
Sensible use with simultaneous supply air humidification in winter with the same pump.
Connection of the recooling /humidification and control of the maximum exhaust air humidity.
Hybrid cooling / recooling
On the exhaust air side, the water-glycol mixture is cooled as close as possible to the wet bulb temperature.
High power density! Use of Mountair Hybaco® elements, using desalinated water.